A middle ear infection is an infection in the space just behind the eardrum, in the area where the ear bones are located. This inflammation is usually caused by bacterial or viral infections and can lead to symptoms such as ear pain, hearing loss and fever.
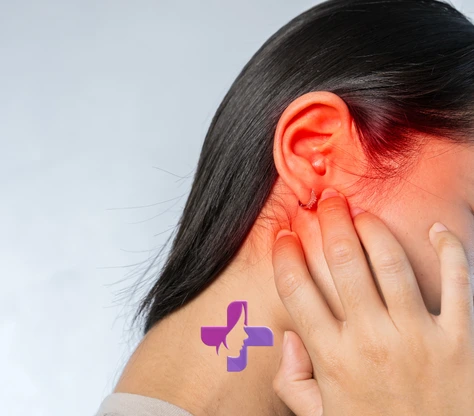
Otitis media in children is a common health problem, especially in infancy and early childhood. This condition, known as “otitis media” in medical language, occurs as a result of infection or inflammation in the middle ear behind the eardrum. In this article, you can find information about the symptoms, causes and treatment methods of otitis media in children.
Symptoms of otitis media in children can vary depending on their age and the severity of the infection. However, the most common symptoms are the following:
Ear Pain: Children may not be able to express ear pain directly, but they may exhibit behaviors such as touching their ears, crying or restlessness.
Loss of Appetite and Sleep Problems: Middle ear inflammation can lead to loss of appetite and disturbed sleep patterns, especially in infants.
Fever: High fever is a common symptom of otitis media in children.
Hearing Problems: Fluid buildup in the middle ear due to infection can temporarily affect children’s hearing.
Balance Problems: Fluid buildup in the middle ear can also affect balance, which can cause children to have difficulty walking.
The main causes of otitis media are:
Colds and Flu: Respiratory infections can cause otitis media because infections in the nose and throat can spread to the ear canal.
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections in particular can cause fluid to build up behind the eardrum and cause infection.
Viral Infections: Viral infections such as flu and colds are among the main causes of otitis media.
Allergic Reactions: Allergies can cause nasal congestion and fluid buildup, leading to otitis media.
Anatomical Factors: The fact that the ear canal is usually short and horizontal in children can cause infections to spread more easily.


Treatment of otitis media varies depending on the type and severity of the infection and the age of the child. Here are common treatment methods:
Antibiotic Treatment: Antibiotic treatment may be needed for bacterial infections. However, antibiotics are not effective for viral infections.
Pain Medication: Painkillers recommended by the doctor can be used to relieve the child’s ear pain.
Removal of Fluid Accumulation: In severe cases, surgical intervention or tube placement may be required to drain the fluid accumulated in the ear.
Allergy Treatment: Antihistamines and other allergy medications may be recommended for otitis media caused by allergic reactions.
Applying Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the ear area can relieve pain and provide relief.
Your child's adenoid problem is treatable and with the right intervention, your child's health can quickly return to normal.
Each of the contents on this site has been prepared for informational purposes. Do not apply any of the treatment methods described on the site without the supervision of a doctor. Otherwise, the site management and Assoc. Prof. will not be responsible in any way for any problems that may arise. Dr. Osman Halit Çam is not responsible.
© 2023 – All Rights Reserved. Assoc. Dr. Osman Halit Cam
Last Updated: 25.07.2025